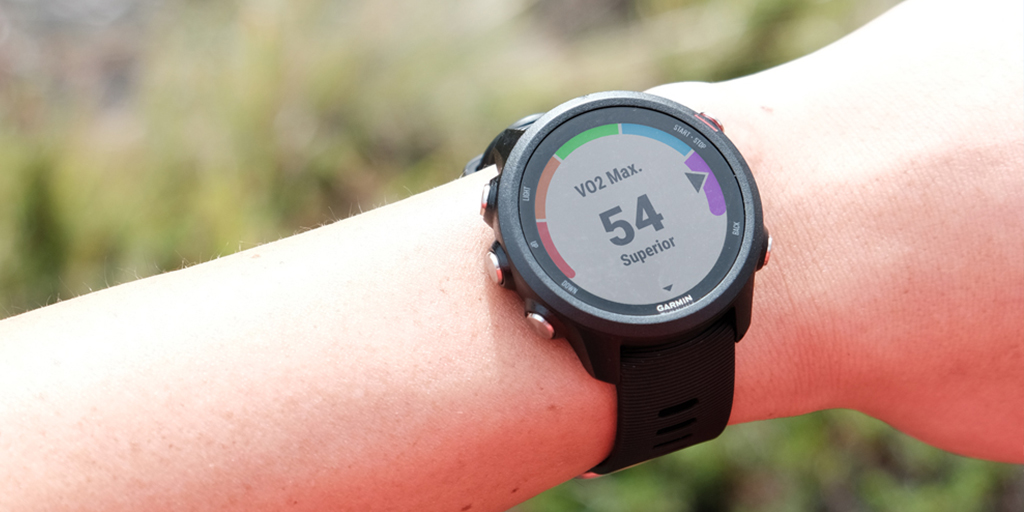
What’s a Good VO2 Max for Me? Your Aerobic Fitness Explained
VO2 max is the number that describes your cardiorespiratory fitness. It’s a single number that captures your heart, lungs, circulatory system, and muscle cells all working independently and together. And not surprisingly, your VO2 max is connected to health, performance and longevity.
At the same time, many people find VO2 max difficult to understand on their Garmin smartwatch. Why? Maybe mixing letters, numbers and abbreviations together makes things look scary and complicated. Let’s skip past that problem for a moment. If you are really interested in fitness, then you will be fine with a funny name.
And in case you were wondering, it is pronounced vee oh two max.
Ask a physiologist about VO2 max and they will explain that it is the maximum volume of oxygen your body can import, transport and utilize in a single minute during intense physical activity. If that rings a bell, then great. You’ve got it and might be ready to scroll down to the VO2 max charts below. There you can instantly see how your VO2 compares to other people of your same age and gender. Otherwise, stick around.
Why VO2 Max Matters
Exercise physiologists have studied how the human body uses oxygen for long time. And the history of VO2 max as a performance metric dates back over a hundred years. Scientists observed that people are always using some oxygen even at rest. Start moving around or exercising and your body starts to use more and more oxygen as the intensity increases.
Why does your body need oxygen? Oxygen is the magical ingredient that makes aerobic energy production possible. That means transforming the energy stored in macronutrients like carbohydrates and fats into fuel for your muscle cells. That is why VO2 max is sometimes referred to as your aerobic capacity. It is also why endurance athletes spend a lot of time working to improve their VO2 max.
To directly measure oxygen consumption, you need to wear a special mask together with a machine capable of analyzing the contents of your respiratory gases. The goal is to measure how much oxygen is in the air you breath in compared to how much oxygen is in the air you exhale. The difference is how much oxygen your body is using.
VO2 max tests are typically performed in a laboratory and involve running on a treadmill. The speed of the treadmill increases gradually until you reach the intensity at which maximum oxygen consumption rate is achieved. It is quite a workout and should only be performed when healthy.
Compatible Garmin watches automatically estimate VO2 max during walking and running activities using a method developed by Firstbeat Analytics. Advanced analytics interpret combinations of heart rate and performance data to reveal your aerobic capacity. This means looking at how quickly you are walking or how fast you are running compared to how hard your body is working to keep up pace. The method can also be used for cycling if you happen to have a power meter mounted on your bike.
Understanding VO2 Max
The first thing to understand is that a higher VO2 max is generally better than a lower VO2 max. A higher VO2 max means that your body is better at taking oxygen from the air and delivering it to your muscles. The more oxygen your muscles can get, the more nutrients you can aerobically transform into the molecular fuel (ATP) that your muscles use to contract and perform. This is important because your aerobic metabolic pathways are by far your most efficient source of energy for your body.
Higher is better than lower, got it. But how high is high enough?
If you are a competitive marathon runner, triathlete, cyclist, or cross-country skier, then the answer is really, really high. Top endurance athletes practically dedicate their lives to improving their VO2 max.
For most people, however, a good VO2 max is understood in terms of so-called normal values. These are the ranges of VO2 max that researchers have identified in the general population. This is where things can get tricky. Similar VO2 max results can mean different things for different people.
A VO2 max of 40 can be excellent for one person, good for another and only poor for a third. What? The missing context here is that the first person is a 28-year-old woman, the second is a 42-year-old man and the last is a 20-year-old male student.
Making sense of VO2 max requires personal context. That is the challenge.
VO2 Max for Men vs. Women
Variation in physical performance between men and women mostly come down to differences in body composition. Research shows that men typically have more lean muscle mass than women. And women tend to naturally accumulate more fatty tissue. Where fat deposits accumulate on the body also varies between men and women. Men tend to store fat around the trunk and abdomen, and women storing more fat around the hips and thighs.
These natural differences in average body composition are important for understanding what your personal VO2 max means. Muscles use oxygen while fat is simply stored energy.
On average, men have higher VO2 max values than women. So for a man and woman with the same VO2 max, the woman will have a better fitness level compared to her peer group.
A top female endurance athlete will almost certainly have a much higher VO2 max than the average male. However, she will likely have a lower VO2 max compared to a top male endurance athlete.
What’s a Good VO2 Max for My Age?
Age is always a tough topic. It is not fun to think about, but our performance tends to get worse as we get older. As humans our peak fitness potential is usually around the age of 20. This is true for both men and women.
From there, fitness typically declines between 5%-20% per decade in healthy individuals between the ages of 20 and 65. Cardiorespiratory fitness losses can be managed through healthy lifestyle choices and regular physical activity. Past the age of 70, fitness levels decline even more quickly.
Several factors contribute to age-related fitness declines. One is the fact that total body mass or weight tends to increase as we get older, but lean muscle mass decreases. Another is that our muscles work less efficiently. This affects the large muscles that power our movement and the heart.
As we get older, our hearts simply cannot beat as fast as when we were younger. The force with which the heart beats to push oxygenated blood to the muscles also decreases.
The good news about VO2 max and aging is that for the most part accelerated fitness declines resulting from sedentary lifestyles can be reversed. This means that with proper care you can improve your fitness and feel younger and more energetic in the process.
Typical VO2 Max Fitness Scores for Men by Age Group:
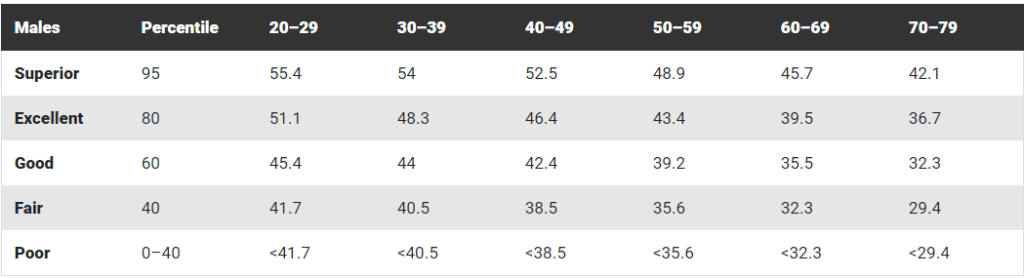
Typical VO2 Max Fitness Scores for Women by Age Group:
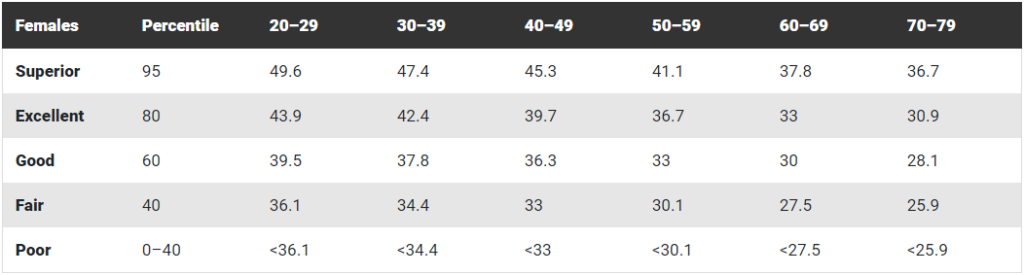
Data reprinted with permission from The Cooper Institute®. For more information, go to www.CooperInstitute.org.
What About My Weight?
Weight management and fitness topics often go together and for good reason. Both are good health indicators and both benefit from healthy lifestyles. When you get your VO2 max from a smartwatch or fitness tracker, the number you see is what exercise scientists call your relative VO2 max.
This simply means that the number you see is how much oxygen you can use per kilogram of body weight in a single minute. That means that your body weight is already factored into the equation.
If you are curious about your absolute VO2 max, you can easily calculate it. Simply multiply the VO2 max shown on your watch by your body weight measured in kilograms.





